中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 139-152.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00116
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-05-15
修回日期:2025-07-10
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-08-18
作者简介:王卫国(1992—),男,山西忻州人,博士,副教授,主要从事生态环境遥感方面的研究。E-mail: wangwg@sxnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Weiguo Wang( ), Huan Xie, Guoqing Feng, Shuzhen Jia
), Huan Xie, Guoqing Feng, Shuzhen Jia
Received:2025-05-15
Revised:2025-07-10
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-08-18
摘要:
作为中国北方核心生态屏障,京津风沙源治理工程区长期面临沙尘暴频发、土地沙化加剧及植被显著退化等复合型生态胁迫,提升生态工程效能对厘清其生态环境质量时空演化机制具有迫切需求。本研究耦合Google Earth Engine(GEE)云平台与多源遥感数据,构建融合热度、绿度、湿度、干度四维特征的遥感生态指数,系统分析2000—2020年京津风沙源二期治理工程区生态环境质量时空分异规律。通过最优参数地理探测器模型定量解析多维驱动因子的独立及交互效应。结果表明:(1)京津风沙源治理工程区2000—2020年生态质量呈上升趋势,生态环境质量为差、较差等级面积减小,一般、良、优等级面积增加;生态环境质量地域差异明显,总体呈现东南部生态环境优越、西北部生态环境恶劣的特点。(2)探究区域生态环境影响因素表明影响因素、分级方法、分级数量均对生态环境质量的解释力产生重要影响。(3)各影响因素对生态环境质量的影响程度不同,年降水量与植被净初级生产力对生态环境质量的影响最显著。
中图分类号:
王卫国, 谢欢, 冯国庆, 家淑珍. 京津风沙源治理工程区生态环境质量及驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 139-152.
Weiguo Wang, Huan Xie, Guoqing Feng, Shuzhen Jia. Ecological environment quality and driving forces in the Beijing-Tianjin Sandstorm Source Control Project area[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(4): 139-152.
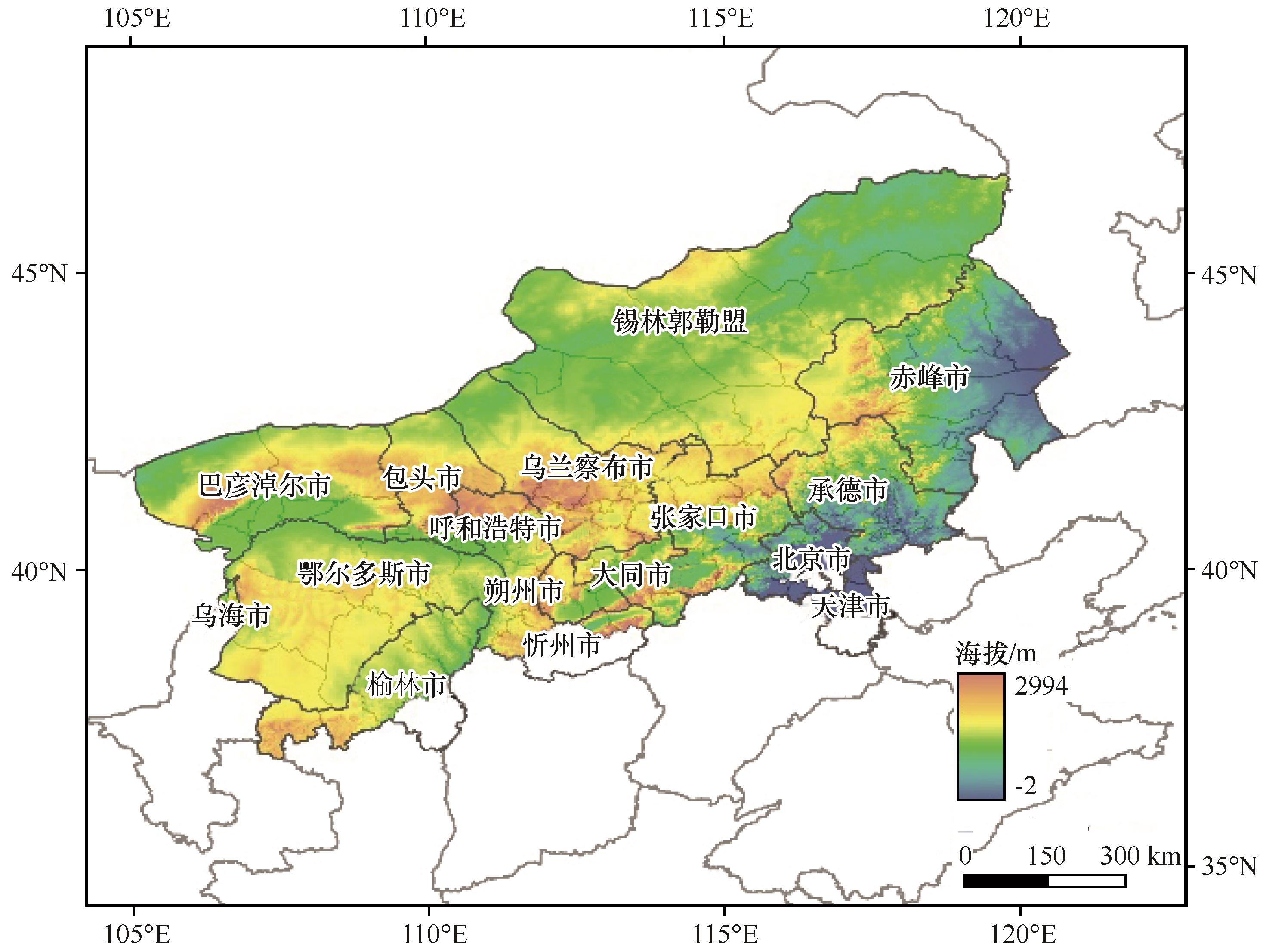
图1 京津风沙源二期治理工程区分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号为GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.1 Distribution of the Beijing-Tianjin Sandstorm Source Control Project Area (BTSSCPA)
| 指标 | 时间(年份) | 时空分辨率 | 数据名 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | 2000—2020 | 500 m | MOD09A1 | GEE |
| WET | ||||
| NDBSI | ||||
| LST | 500 m | MOD11A2 | ||
| 人口 | 1年,1 000 m | LandScan Global | 美国橡树岭实验室 | |
| GDP | 2000 | 5年,1 000 m | 中国GDP空间分布公里网格数据集 | 中国科学院 资源环境科学 与数据中心 |
| 土地利用 | 2005 | 5年,30 m | 中国多时期土地利用遥感监测数据集 | |
| 2010 | ||||
| 2015 | ||||
| 2020 | ||||
| 年均气温 | 2000—2020 | 1年,1 000 m | 中国气象要素年度空间插值数据集 | |
| 年降水量 | 1年,1 000 m | |||
| NPP | 5年,500 m | MOD17A3 | 美国地质调查局 | |
| 高程 | — | 30 m | ASTER GDEM 30 m分辨率数字高程数据 | 地理空间数据云平台 |
| 土壤有机质含量 | 2023 | 1000 m | HWSD | 联合国粮农组织 |
表1 数据源基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of data sources
| 指标 | 时间(年份) | 时空分辨率 | 数据名 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | 2000—2020 | 500 m | MOD09A1 | GEE |
| WET | ||||
| NDBSI | ||||
| LST | 500 m | MOD11A2 | ||
| 人口 | 1年,1 000 m | LandScan Global | 美国橡树岭实验室 | |
| GDP | 2000 | 5年,1 000 m | 中国GDP空间分布公里网格数据集 | 中国科学院 资源环境科学 与数据中心 |
| 土地利用 | 2005 | 5年,30 m | 中国多时期土地利用遥感监测数据集 | |
| 2010 | ||||
| 2015 | ||||
| 2020 | ||||
| 年均气温 | 2000—2020 | 1年,1 000 m | 中国气象要素年度空间插值数据集 | |
| 年降水量 | 1年,1 000 m | |||
| NPP | 5年,500 m | MOD17A3 | 美国地质调查局 | |
| 高程 | — | 30 m | ASTER GDEM 30 m分辨率数字高程数据 | 地理空间数据云平台 |
| 土壤有机质含量 | 2023 | 1000 m | HWSD | 联合国粮农组织 |
| 年份 | NDVI | LST | WET | NDBSI | 特征值 | 贡献率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | PC1 | 0.56 | -0.42 | 0.46 | -0.55 | 0.16 | 84 |
| PC2 | 0.51 | -0.15 | -0.84 | -0.07 | 0.02 | 9 | |
| PC3 | -0.38 | -0.89 | -0.08 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 5 | |
| PC4 | 0.54 | -0.04 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 2 | |
| 2005 | PC1 | 0.55 | -0.40 | 0.51 | -0.52 | 0.22 | 91 |
| PC2 | 0.37 | -0.38 | -0.83 | -0.13 | 0.01 | 5 | |
| PC3 | -0.33 | -0.82 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 3 | |
| PC4 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 1 | |
| 2010 | PC1 | 0.55 | -0.41 | 0.51 | -0.52 | 0.20 | 90 |
| PC2 | 0.39 | -0.30 | -0.85 | -0.18 | 0.01 | 5 | |
| PC3 | -0.23 | -0.83 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 3 | |
| PC4 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 2 | |
| 2015 | PC1 | 0.56 | -0.42 | 0.49 | -0.53 | 0.22 | 89 |
| PC2 | 0.34 | -0.39 | -0.85 | -0.11 | 0.01 | 6 | |
| PC3 | -0.17 | -0.75 | 0.20 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 3 | |
| PC4 | -0.74 | -0.33 | -0.07 | -0.58 | 0.00 | 2 | |
| 2020 | PC1 | 0.56 | -0.39 | 0.50 | -0.53 | 0.21 | 90 |
| PC2 | -0.33 | 0.56 | 0.76 | -0.06 | 0.01 | 5 | |
| PC3 | -0.27 | -0.65 | 0.41 | 0.58 | 0.01 | 4 | |
| PC4 | -0.71 | -0.33 | -0.12 | -0.62 | 0.00 | 1 |
表2 京津风沙源二期治理工程区2000、2005、2010、2015、2020年各指标主成分分析结果
Table 2 Results of PCA of four indexes in the BTSSCPA at the year of 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015 and 2020
| 年份 | NDVI | LST | WET | NDBSI | 特征值 | 贡献率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | PC1 | 0.56 | -0.42 | 0.46 | -0.55 | 0.16 | 84 |
| PC2 | 0.51 | -0.15 | -0.84 | -0.07 | 0.02 | 9 | |
| PC3 | -0.38 | -0.89 | -0.08 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 5 | |
| PC4 | 0.54 | -0.04 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 2 | |
| 2005 | PC1 | 0.55 | -0.40 | 0.51 | -0.52 | 0.22 | 91 |
| PC2 | 0.37 | -0.38 | -0.83 | -0.13 | 0.01 | 5 | |
| PC3 | -0.33 | -0.82 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 3 | |
| PC4 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 1 | |
| 2010 | PC1 | 0.55 | -0.41 | 0.51 | -0.52 | 0.20 | 90 |
| PC2 | 0.39 | -0.30 | -0.85 | -0.18 | 0.01 | 5 | |
| PC3 | -0.23 | -0.83 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.01 | 3 | |
| PC4 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 2 | |
| 2015 | PC1 | 0.56 | -0.42 | 0.49 | -0.53 | 0.22 | 89 |
| PC2 | 0.34 | -0.39 | -0.85 | -0.11 | 0.01 | 6 | |
| PC3 | -0.17 | -0.75 | 0.20 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 3 | |
| PC4 | -0.74 | -0.33 | -0.07 | -0.58 | 0.00 | 2 | |
| 2020 | PC1 | 0.56 | -0.39 | 0.50 | -0.53 | 0.21 | 90 |
| PC2 | -0.33 | 0.56 | 0.76 | -0.06 | 0.01 | 5 | |
| PC3 | -0.27 | -0.65 | 0.41 | 0.58 | 0.01 | 4 | |
| PC4 | -0.71 | -0.33 | -0.12 | -0.62 | 0.00 | 1 |
| 年份 | 差 | 较差 | 一般 | 良 | 优 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
面积 /万km2 | 比例 /% | 面积 /万km2 | 比例 /% | 面积 /万km2 | 比例/% | 面积 /万km2 | 比例/% | 面积 /万km2 | 比例 /% | |
| 2000 | 22.9 | 31.4 | 24.0 | 32.9 | 14.6 | 20.0 | 7.1 | 9.7 | 4.4 | 6.0 |
| 2005 | 21.9 | 30.0 | 18.8 | 25.8 | 16.5 | 22.6 | 8.9 | 12.2 | 6.9 | 9.4 |
| 2010 | 19.5 | 26.7 | 25.2 | 34.5 | 14.1 | 19.3 | 7.9 | 10.8 | 6.3 | 8.7 |
| 2015 | 19.6 | 26.8 | 20.3 | 27.8 | 16.4 | 22.5 | 9.3 | 12.7 | 7.4 | 10.2 |
| 2020 | 15.7 | 21.5 | 19.5 | 26.7 | 18.8 | 25.8 | 11.0 | 15.1 | 8.0 | 10.9 |
表3 京津风沙源二期治理工程区生态环境质量各等级面积和比例
Table 3 Area and ratio on the different classes of ecological quality in the BTSSCPA from 2000 to 2020
| 年份 | 差 | 较差 | 一般 | 良 | 优 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
面积 /万km2 | 比例 /% | 面积 /万km2 | 比例 /% | 面积 /万km2 | 比例/% | 面积 /万km2 | 比例/% | 面积 /万km2 | 比例 /% | |
| 2000 | 22.9 | 31.4 | 24.0 | 32.9 | 14.6 | 20.0 | 7.1 | 9.7 | 4.4 | 6.0 |
| 2005 | 21.9 | 30.0 | 18.8 | 25.8 | 16.5 | 22.6 | 8.9 | 12.2 | 6.9 | 9.4 |
| 2010 | 19.5 | 26.7 | 25.2 | 34.5 | 14.1 | 19.3 | 7.9 | 10.8 | 6.3 | 8.7 |
| 2015 | 19.6 | 26.8 | 20.3 | 27.8 | 16.4 | 22.5 | 9.3 | 12.7 | 7.4 | 10.2 |
| 2020 | 15.7 | 21.5 | 19.5 | 26.7 | 18.8 | 25.8 | 11.0 | 15.1 | 8.0 | 10.9 |
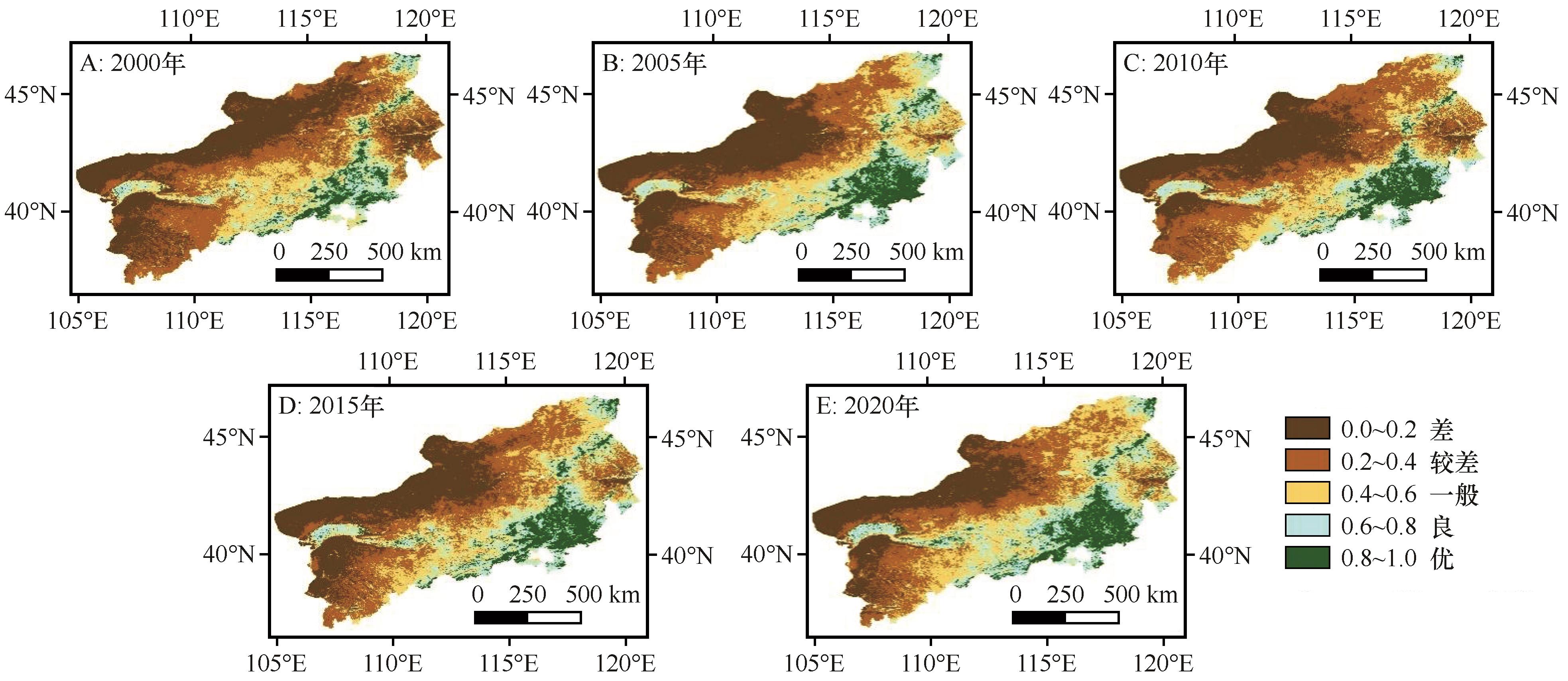
图4 京津风沙源二期治理工程区生态环境质量各等级空间分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号为GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of different classes of ecological quality in the BTSSCPA
| 探测指标 | 2000年 | 2010年 | 2020年 | 2000—2020年平均 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q值 | 排序 | q值 | 排序 | q值 | 排序 | q值 | 排序 | |
| 年降水量 | 0.593 | 1 | 0.574 | 2 | 0.502 | 2 | 0.556 | 2 |
| NPP | 0.567 | 2 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.825 | 1 | 0.729 | 1 |
| 生境质量指数 | 0.421 | 3 | 0.406 | 4 | 0.242 | 6 | 0.356 | 4 |
| 坡度 | 0.355 | 4 | 0.376 | 5 | 0.326 | 4 | 0.352 | 5 |
| 土地利用强度 | 0.341 | 5 | 0.410 | 3 | 0.376 | 3 | 0.376 | 3 |
| GDP | 0.328 | 6 | 0.279 | 6 | 0.267 | 5 | 0.291 | 6 |
| 水土流失指数 | 0.247 | 7 | 0.262 | 7 | 0.241 | 7 | 0.250 | 7 |
| 人口密度 | 0.239 | 8 | 0.154 | 10 | 0.143 | 9 | 0.179 | 9 |
| 土壤有机质含量 | 0.218 | 9 | 0.239 | 8 | 0.231 | 8 | 0.229 | 8 |
| 高程 | 0.151 | 10 | 0.156 | 9 | 0.134 | 10 | 0.147 | 10 |
| 年均气温 | 0.063 | 11 | 0.079 | 11 | 0.072 | 11 | 0.071 | 11 |
表4 影响指标 q 值表
Table 4 Area and ratio on the different classes of ecological quality in the BTSSCPA from 2000 to 2020
| 探测指标 | 2000年 | 2010年 | 2020年 | 2000—2020年平均 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q值 | 排序 | q值 | 排序 | q值 | 排序 | q值 | 排序 | |
| 年降水量 | 0.593 | 1 | 0.574 | 2 | 0.502 | 2 | 0.556 | 2 |
| NPP | 0.567 | 2 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.825 | 1 | 0.729 | 1 |
| 生境质量指数 | 0.421 | 3 | 0.406 | 4 | 0.242 | 6 | 0.356 | 4 |
| 坡度 | 0.355 | 4 | 0.376 | 5 | 0.326 | 4 | 0.352 | 5 |
| 土地利用强度 | 0.341 | 5 | 0.410 | 3 | 0.376 | 3 | 0.376 | 3 |
| GDP | 0.328 | 6 | 0.279 | 6 | 0.267 | 5 | 0.291 | 6 |
| 水土流失指数 | 0.247 | 7 | 0.262 | 7 | 0.241 | 7 | 0.250 | 7 |
| 人口密度 | 0.239 | 8 | 0.154 | 10 | 0.143 | 9 | 0.179 | 9 |
| 土壤有机质含量 | 0.218 | 9 | 0.239 | 8 | 0.231 | 8 | 0.229 | 8 |
| 高程 | 0.151 | 10 | 0.156 | 9 | 0.134 | 10 | 0.147 | 10 |
| 年均气温 | 0.063 | 11 | 0.079 | 11 | 0.072 | 11 | 0.071 | 11 |
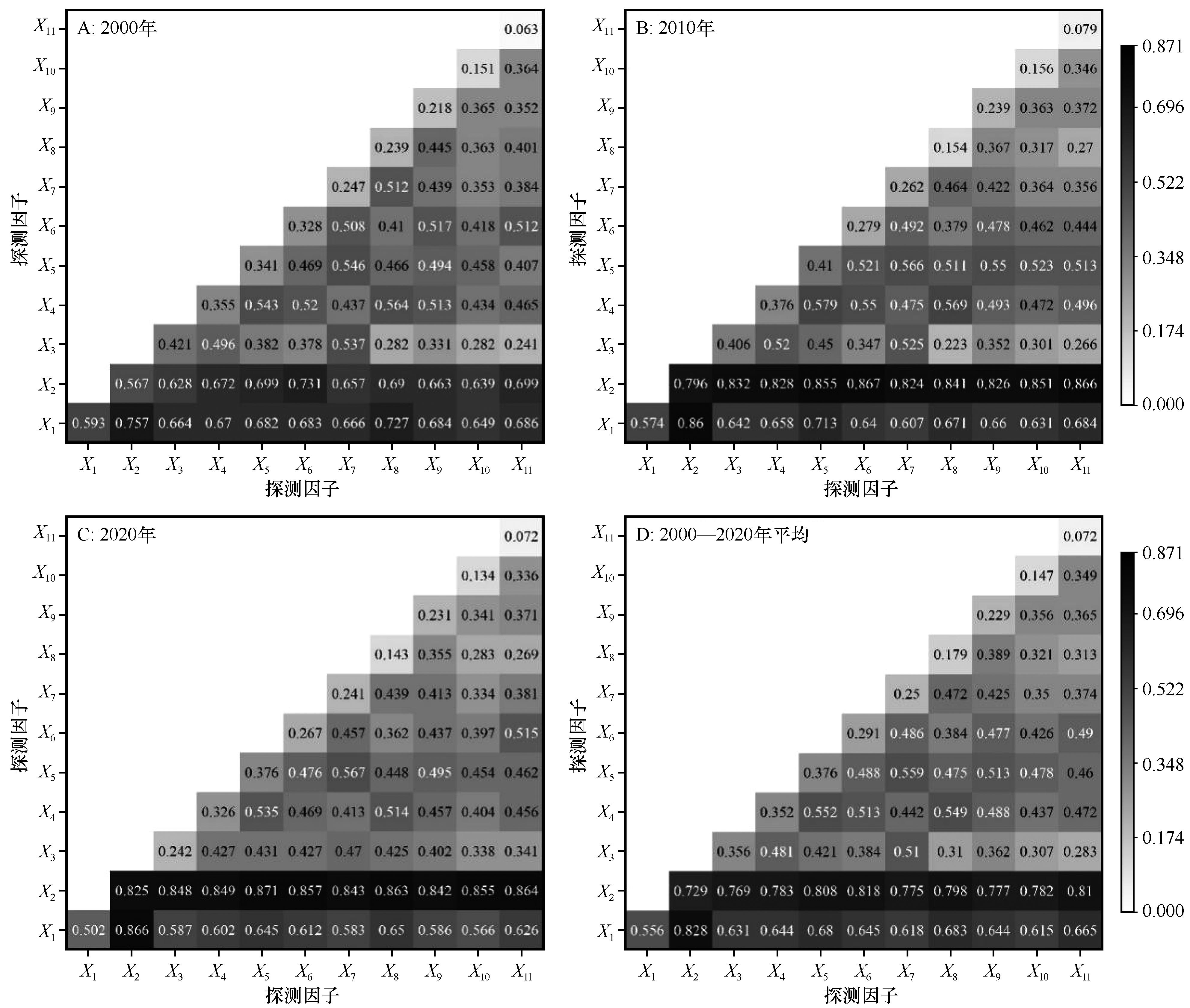
图7 京津风沙源二期治理工程区影响因素交互作用探测结果注:X1:年降水量;X2:NPP;X3:生境质量指数;X4:坡度;X5:土地利用强度;X6:GDP;X7:水土流失指数;X8:人口密度;X9:土壤有机质含量;X10:高程;X11:年均气温
Fig.7 Detection results of the interaction of driving factors in BTSSCPA
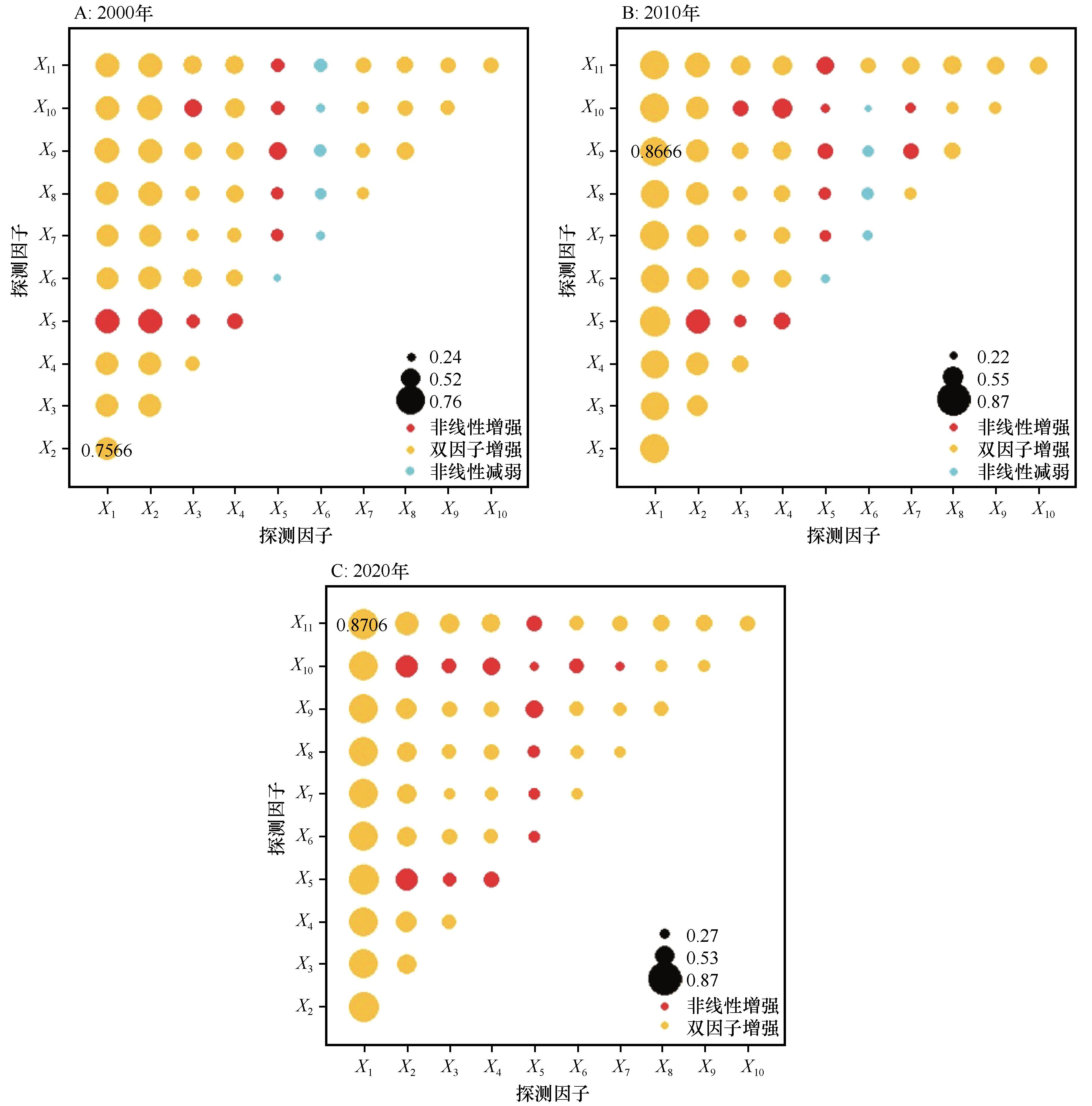
图8 京津风沙源二期治理工程区影响因素交互作用类型探测结果注:X1:NPP;X2:年降水量;X3:水土流失指数;X4:坡度;X5:年均气温;X6:生境质量指数;X7:高程;X8:土壤有机质含量;X9:GDP;X10:人口密度;X11:土地利用强度
Fig.8 Detection results of the interaction type of driving factors in BTSSCPA
| [1] | 雷燕慧,丁国栋,李梓萌,等.京津风沙源治理工程区土地利用/覆盖变化及生态系统服务价值响应[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(6):29-40. |
| [2] | 崔晓,赵媛媛,丁国栋,等.京津风沙源治理工程区植被对沙尘天气的时空影响[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(12):171-179. |
| [3] | 黄麟,吴丹,孙朝阳.基于规划目标的京津风沙源治理区生态保护与修复效应[J].生态学报,2020,40(6):1923-1932. |
| [4] | 章程焱,杨少康,董晓华,等.基于RSEI指数的长江上游流域生态环境质量时空演变及影响因子研究[J].水土保持研究,2023,30(1):356-363. |
| [5] | 徐涵秋.城市遥感生态指数的创建及其应用[J].生态学报,2014,33(24):7853-7862. |
| [6] | 徐涵秋.区域生态环境变化的遥感评价指数[J].中国环境科学,2013,33(5):889-897. |
| [7] | Xiong Y, Xu W, Lu N,et al.Assessment of spatial-temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE:a case study in Erhai Lake Basin,Yunnan Province,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2021,125:107518. |
| [8] | Chen Z, Chen R, Guo Q,et al.Spatiotemporal change of urban ecologic environment quality based on RSEI:taking Meizhou City,China as an example[J].Sustainability,2022,14(20):13424. |
| [9] | 邵全琴,刘树超,宁佳,等.2000-2019年中国重大生态工程生态效益遥感评估[J].地理学报,2022,77(9):2133-2153. |
| [10] | 徐涵秋.利用改进的归一化差异水体指数(MNDWI)提取水体信息的研究[J].遥感学报,2005,9(5):589-595. |
| [11] | 徐勇,郑梓聪,曹泳茵,等.4种典型人口空间化产品精度的比较评价[J].广州大学学报(自然科学版),2023,22(4):20-28. |
| [12] | 汤从沧,李巧,陶洪飞,等.基于改进遥感生态指数模型的塔里木河流域生态环境质量评价[J].环境科学,2025,46(7):4485-4498. |
| [13] | Xu Y, Yang X, Xing X,et al.Coupling eco-environmental quality and ecosystem services to delineate priority ecological reserves-a case study in the Yellow River Basin[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2024,365:121645. |
| [14] | 岳奕帆,赵文智,刘任涛,等.宁夏荒漠草原带生态环境质量时空变化及驱动机制研究[J].生态学报,2024,44(20):9067-9080. |
| [15] | 薛桦,刘萍.基于RSEI的黄河中游地区生态环境质量时空演化特征及驱动因素:以延安市为例[J].水土保持研究,2024,31(1):373-384. |
| [16] | 崔亚婷,李嬛,郑龙啸,等.基于RSEI的黄河上游流域生态环境质量变化分析[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):107-118. |
| [17] | Hall L, Krausman P, Morrison M.The habitat concept and a plea for standard technology[J].Wildlife Society Bulletin,1997,25(1):173-182. |
| [18] | 孙菲菲,张增祥,左丽君,等.土地利用强度研究进展、瓶颈问题与前景展望[J].草业科学,2020,37(7):1259-1271. |
| [19] | Liu M, Dong X, Wang X,et al.The trade-offs/synergies and their spatial-temporal characteristics between ecosystem services and human well-being linked to land-use change in the Capital Region of China[J].Land,2022,11(5):749. |
| [20] | 郭泽呈,魏伟,石培基,等.中国西北干旱区土地沙漠化敏感性时空格局[J].地理学报,2020,75(9):1948-1965. |
| [21] | Renard K G.Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE)[M].Washington DC,USA:United States Government Printing,1997:118-141. |
| [22] | 章文波.不同类型雨量资料估算降雨侵蚀力[J].资源科学,2003,25(1):35-41. |
| [23] | Williams J R.EPIC-erosion/productivity impact calculator:1.model documentation[J].Technical Bulletin-United States Department of Agriculture,1990,4(4):206-207. |
| [24] | Desmet P J J, Govers G.A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLELS factor on topographically complex landscape units[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,1996,51(5):427-433. |
| [25] | 王劲峰,徐成东.地理探测器:原理与展望[J].地理学报,2017,72(1):116-134. |
| [26] | 袁静芳,周海丽,张星烁,等.京津风沙源治理区植被固碳能力估算及归因分析[J].生态学报,2024,44(15):6731-6743. |
| [27] | Xing X, Yang X, Guo J,et al.Response of ecosystem services in Beijing-Tianjin Sandstorm Source Control Project to differing engineering measures scenarios[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2023,384:135573. |
| [28] | 赵恒谦,刘轩绮,刘哿,等.京津风沙源区NPP时空变化及其对治理工程实施的响应[J].生态学报,2024,44(6):2406-2419. |
| [29] | Niu L, Shao Q, Ning J,et al.The assessment of ecological restoration effects on Beijing-Tianjin Sandstorm Source Control Project area during 2000-2019[J].Ecological Engineering,2023,186:106831. |
| [30] | Li C, Gao Z, Sun B,et al.Ecological restoration effects of the Beijing-Tianjin Sandstorm Source Control Project in China since 2000[J].Ecological Indicators,2023,146:109782. |
| [31] | 吴波.京津风沙源治理工程助力生态建设高质量发展[J].科学通报,2023,68(11):1284-1285. |
| [32] | 李晓松,张磊,姬翠翠,等.2000-2018年京津风沙源沙化土地时空动态与归因分析[J].科学通报,2023,68(11):1343-1355. |
| [33] | 赵晓萌,程宏,蒋宁,等.京津风沙源土壤风蚀时空格局及其演化[J].科学通报,2023,68():238-253. |
| [34] | 迟文峰,匡文慧,贾静,等.京津风沙源治理工程区LUCC及土壤风蚀强度动态遥感监测研究[J].遥感技术与应用,2018,33(5):965-974. |
| [35] | 辛会超,郭玮,王贺封.基于GEE和RSEI的京津冀地区生态环境质量时序动态评估[J].西北林学院学报,2024,39(2):106-114. |
| [36] | 杨泽康,田佳,李万源,等.黄河流域生态环境质量时空格局与演变趋势[J].生态学报,2021,41(19):7627-7636. |
| [37] | 孟琪,武志涛,杜自强,等.京津风沙源区不同分区植被覆盖度变化及归因分析[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(8):2895-2905. |
| [38] | 张彪,王爽,李庆旭,等.京津风沙源治理工程区水源涵养功能时空变化分析[J].生态学报,2021,41(19):7530-7541. |
| [39] | Yue Y, Shi P, Zou X,et al.The measurement of wind erosion through field survey and remote sensing:a case study of the Mu Us Desert, China[J].Natural Hazards,2015,76(3):1497-1514. |
| [40] | 武旭,王勃砚,任伟,等.2000-2022年黄河流域甘肃段生态环境质量与影响因素[J].应用生态学报,2025,36(2):353-364. |
| [1] | 陈兵兵, 盖迎春, 宋忠航, 吴向楠, 艾宇, 杨映, 王生棠, 刘宇烁. 祁连山地区生态质量时空变化及驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 258-267. |
| [2] | 苏万峰, 汉光昭, 叶得力, 曹广超. 共和盆地生态环境遥感评价及驱动力分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 74-84. |
| [3] | 崔亚婷, 李嬛, 郑龙啸, 吴孟泉. 基于 RSEI 的黄河上游流域生态环境质量变化分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 107-118. |
| [4] | 刘凯露, 吴新萍, 刘永强, 买买提艾力·买买提依明null, 杨帆, 何清. 基于多源遥感与再分析数据估算塔克拉玛干沙漠地表净辐射日变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 51-61. |
| [5] | 贾浩巍, 颜长珍, 邢学刚, 谢家丽, 冯坤. 基于改进的遥感生态指数(MRSEI)的青海省都兰县生态环境质量评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 181-190. |
| [6] | 武磊, 李常斌, 王刘明, 谢旭红, 张媛, 魏健美. 基于ESA-LUC和MODIS-NDVI的西北干旱荒漠-绿洲体系分类阈值及应用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 139-150. |
| [7] | 李志鹏, 曹晓明, 丁杰, 冯益明. MODIS卫星影像显示的2001-2017年中国荒漠化年度状况[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 135-140. |
| [8] | 张佳琦, 张勃, 马彬, 曹博, 梁晶晶, 马尚谦. 三江平原NDVI时空变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(3): 206-213. |
| [9] | 热伊莱·卡得尔, 玉苏甫·买买提, 玉素甫江·如素力, 阿迪来·乌甫, 艾则孜提约麦尔·麦麦提, 姜红. 伊犁河谷2001-2014年地表温度时空分异特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(3): 637-644. |
| [10] | 李火青, 吴新萍, 买买提艾力·买买提依明, 霍文, 杨兴华, 杨帆, 何清, 刘永强. 基于FTIR和MODIS数据估算新疆沙漠宽波段地表比辐射率[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(3): 523-529. |
| [11] | 沙莎, 郭铌, 李耀辉, 胡蝶, 王丽娟. 温度植被干旱指数(TVDI)在陇东土壤水分监测中的适用性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(1): 132-139. |
| [12] | 康文平, 刘树林, 段翰晨. 基于MODIS时间序列数据的沙漠化遥感监测及沙漠化土地图谱分析——以内蒙古中西部地区为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(2): 307-318. |
| [13] | 边多, 杨秀海, 普布次仁, 罗布, 吉律, 刘奎军. 西藏NPP时空格局与气候因子的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(3): 830-836. |
| [14] | 邓煜霖, 塔西甫拉提·特依拜, 姜红涛, 张飞, 买买提·沙吾提, 努尔麦麦提江·吾布力卡斯穆. 艾比湖流域NDVI垂直梯度变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(2): 508-513. |
| [15] | 姜红涛, 塔西甫拉提·特依拜, 阿尔达克·克里木, 张飞, 买买提·沙吾提, 吴雪梅. 艾比湖流域NDVI变化及其与降水、温度的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(6): 1678-1684. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
